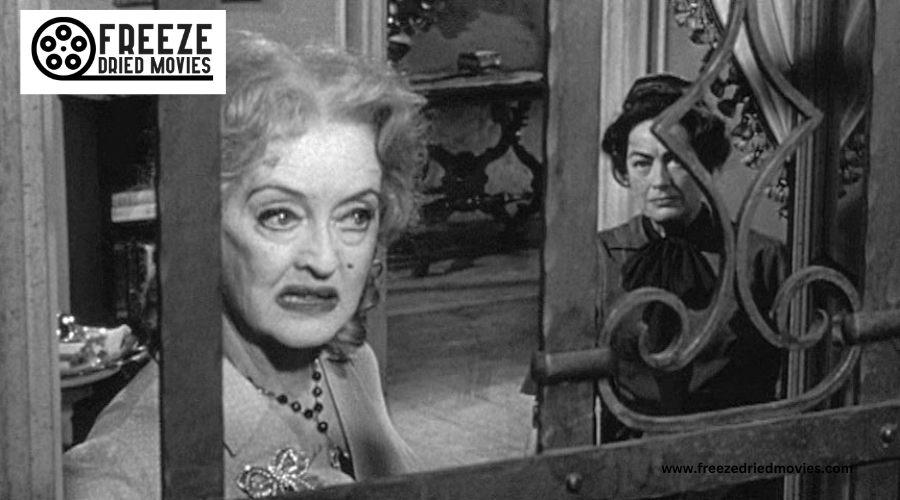
The Horror Timeline: Early 20th Century - Shaping Modern Fear in Literature and Film
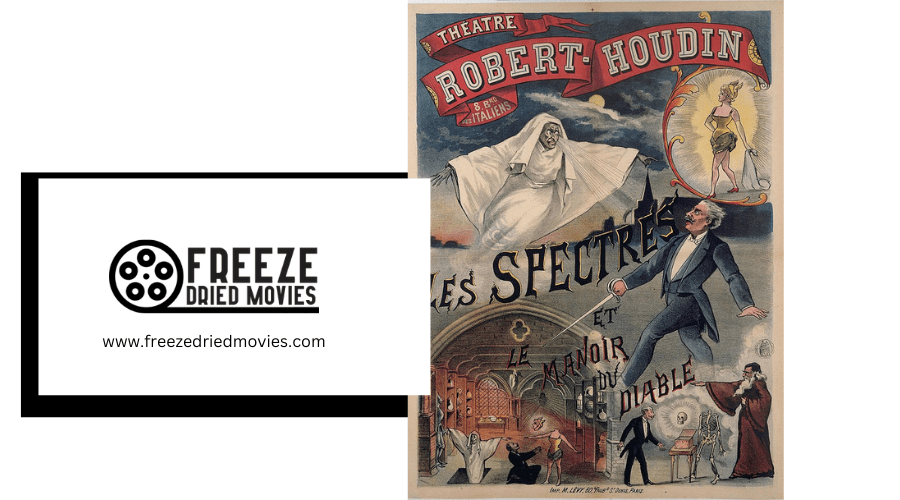
Horror movies have captivated audiences for over a century. The genre emerged in the early 1900s, with silent films like "Le Manoir du Diable" paving the way. As technology advanced, horror cinema evolved to include sound, special effects, and new storytelling techniques.
The 1920s saw the release of influential films like "Nosferatu," which set the stage for future vampire tales. German filmmakers of this era experimented with stories about artificial creatures, adding a new dimension to horror. As the genre grew, it drew inspiration from classic literature and plays, incorporating elements from works by Shakespeare, Marlowe, and others.
A History of Frights
The Early Years

The dawn of the 20th century marked a new era for scary stories and films. In 1902, W.W. Jacobs penned "The Monkey's Paw," a tale that became one of the most famous short horror stories. That same year, Joseph Conrad's "Heart of Darkness" explored the darker side of human nature.
Ghost stories gained popularity with M.R. James's 1904 collection "Ghost Stories of an Antiquary." Algernon Blackwood's "The Listener" followed in 1907, featuring his renowned work "The Willows."
Early horror films emerged in this period. The 16-minute "Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde" (1908) is considered one of the first true horror movies. German filmmakers experimented with artificial creature stories, producing works like "Der Golem" (1914) and "Homunculus" (1916).
The Roaring Twenties

The 1920s saw a boom in horror culture. "Nosferatu" (1922), directed by F.W. Murnau, brought vampires to the silver screen. That same year, the discovery of King Tut's tomb sparked rumors of ancient curses.
"Weird Tales" magazine debuted in 1923, providing a platform for fantasy and horror writers. H.P. Lovecraft, a frequent contributor, began developing his Cthulhu Mythos with stories like "The Nameless City."
Universal Studios produced silent film versions of classic tales, including "The Hunchback of Notre Dame" (1923) and "The Phantom of the Opera" (1925), both starring Lon Chaney Sr.
The Golden Age of Monster Movies

The 1930s ushered in the golden age of monster movies. Universal Studios led the charge with films like "Dracula" and "Frankenstein" in 1931. These movies established horror icons that endure today.
"The Mummy" (1932) capitalized on the public's fascination with Egyptian archaeology. "The Wolf Man" (1941) added werewolves to Universal's monster roster.
Alfred Hitchcock began his career in this era, directing "The Lodger" in 1927 and "Psycho" in 1960, pushing the boundaries of psychological horror.
Post-War Frights

The atomic age brought new fears to the forefront. "Godzilla" (1954) reflected anxieties about nuclear weapons. Richard Matheson's novel "I Am Legend" (1954) blended science fiction with vampire lore.
Demonic possession became a popular theme, culminating in William Peter Blatty's "The Exorcist" (1971). Shirley Jackson's "The Haunting of Hill House" (1959) set the standard for haunted house stories.
The Rise of Slashers
The late 1960s saw a shift toward more graphic horror. George A. Romero's "Night of the Living Dead" (1968) reinvented zombie films and sparked a new subgenre.
Influential Figures
Throughout this period, several key figures shaped the horror genre:
- Lon Chaney Sr.: Known as "The Man of a Thousand Faces," he starred in silent horror classics.
- Alfred Hitchcock: His psychological thrillers redefined suspense in film.
- H.P. Lovecraft: His cosmic horror stories influenced countless writers and filmmakers.
- Universal Studios: Their monster movies of the 1930s and 1940s created enduring horror icons.
Literary Landmarks

Horror literature evolved alongside film:
- "Frankenstein" (1818) by Mary Shelley
- "Dracula" (1897) by Bram Stoker
- "The Castle of Otranto" (1764) by Horace Walpole (considered the first Gothic novel)
- "The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde" (1886) by Robert Louis Stevenson
Subgenres and Themes
Various subgenres emerged during this time:
- Supernatural Horror
- Psychological Horror
- Monster Movies
- Slasher Films
- Cosmic Horror
Common themes included:
- Mad scientists
- Vampires and werewolves
- Haunted houses
- Demonic possession
- Atomic age fears
Impact on Popular Culture
Horror films and literature shaped popular culture in many ways:
- Created enduring characters (Dracula, Frankenstein's monster)
- Influenced fashion and art
- Sparked public debates about censorship
- Reflected societal fears and anxieties
Notable Works
| Year | Title | Creator | Medium |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1910 | First Frankenstein Film | J. Searle Dawley | Film |
| 1922 | Nosferatu | F.W. Murnau | Film |
| 1925 | The Phantom of the Opera | Rupert Julian | Film |
| 1931 | Dracula | Tod Browning | Film |
| 1954 | I Am Legend | Richard Matheson | Novel |
| 1959 | The Haunting of Hill House | Shirley Jackson | Novel |
| 1968 | Night of the Living Dead | George A. Romero | Film |




